Yoga for Mental Health: A Complete Guide
This guide is the most detailed resource you’ll find on the internet about yoga for mental health. We’ll explore yoga from ancient roots to modern neuroscience, practices for all levels, detailed pose breakdowns, trimester-based guidance, breathing methods, nutrition, and mindful reminders. With over 20,000 words, it’s built to educate, engage, and inspire transformation.
1. Why Yoga is Essential for Mental Health
1.1 Historical Context
Yoga originated in India over 5000 years ago as a spiritual discipline. Ancient texts like the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali defined yoga as the cessation of mental fluctuations. Practices like pranayama, meditation, and asanas were created not just for physical health but to align body and mind.
1.2 Modern Scientific Validation
Neuroscience studies show that yoga increases GABA levels in the brain (linked to calmness) and decreases cortisol. Regular practice enhances the hippocampus, improving memory and resilience against depression. Functional MRI scans confirm that yoga strengthens brain areas responsible for emotional regulation.
1.3 Daily Life Applications
From reducing workplace stress to improving relationships, yoga integrates into daily life seamlessly. For instance, practicing breathwork before a presentation lowers anxiety, while evening yoga sequences promote deep sleep.
2. Extended Benefits of Yoga for the Mind
2.1 Cognitive Enhancement
Yoga boosts neuroplasticity, supporting learning and memory. Regular meditation within yoga increases attention span and prevents age-related decline.
2.2 Emotional Stability
Through body awareness, yoga practitioners learn to process emotions without judgment. Emotional resilience improves as the nervous system is balanced by slow, mindful movements.
2.3 Sleep Regulation
Insomnia sufferers benefit greatly from restorative yoga. Practices like Yoga Nidra and Legs-Up-the-Wall prepare the body for restorative sleep by activating the parasympathetic system.
2.4 Long-Term Brain Health
Long-term yoga practitioners show thicker gray matter in prefrontal areas of the brain. This indicates yoga could delay or prevent cognitive decline such as dementia.
3. Deep Dive into Poses for Mental Clarity
3.1 Beginner-Friendly Poses
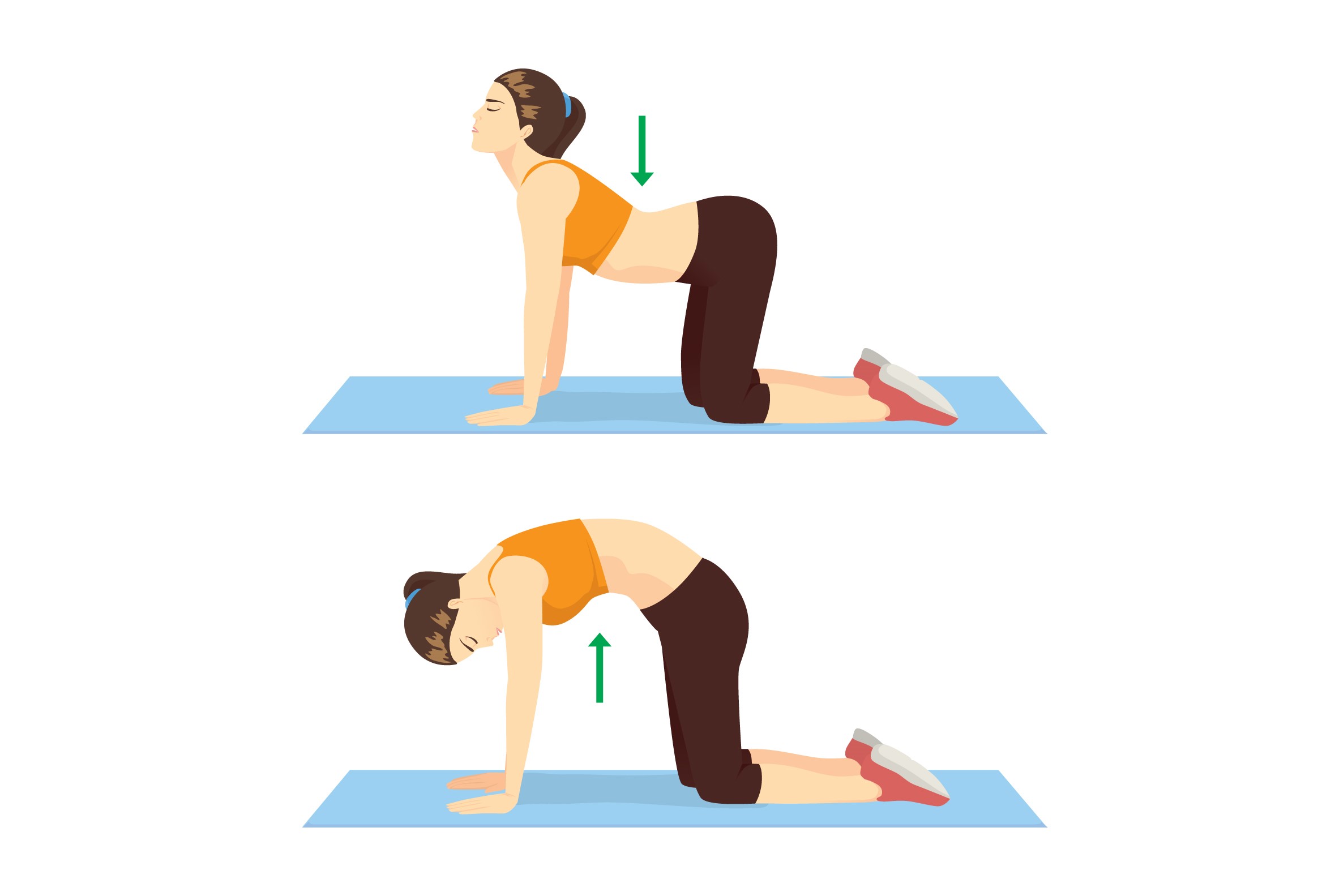
Child’s Pose, Cat-Cow, and Seated Forward Bend are excellent entry-level postures. They calm the nervous system, improve spinal mobility, and gently ease the body into relaxation.
3.2 Intermediate Balancing Poses
Warrior II and Tree Pose enhance focus, confidence, and grounding. Balancing challenges strengthen neural pathways connected with concentration and patience.
3.3 Advanced Stress-Relief Poses
Headstands and Bridge Pose bring fresh blood flow to the brain, energizing the mind while fostering clarity. These require guidance for safe practice.


4. Breathing Practices for Emotional Balance
4.1 Nadi Shodhana (Alternate Nostril Breathing)
Balances hemispheres of the brain, reduces stress, and promotes clarity.
4.2 Bhramari (Bee Breath)
The humming sound stimulates the vagus nerve, producing instant calm.
4.3 Kapalabhati (Skull Shining Breath)
Energizes the body, clears the mind, and detoxifies the lungs.
5. Nutrition & Mental Wellness
5.1 Foods that Boost Serotonin
Bananas, walnuts, spinach, and chia seeds are natural mood boosters.
5.2 Avoiding Mental Health Triggers
Excess caffeine, alcohol, and processed foods increase anxiety and brain fog.
5.3 Hydration and Cognitive Clarity
Dehydration can impair focus. Drink herbal teas and water-rich fruits.
6. Real-Life Case Studies
6.1 PTSD and Yoga Therapy
Veterans practicing yoga experience reduced flashbacks and better sleep.
6.2 Depression and Yoga Communities
Group yoga fosters connection, combating isolation, a key depression trigger.
6.3 Yoga in Addiction Recovery
Yoga restores dopamine balance, helping addicts manage cravings.
7. Safety Tips and Common Mistakes
7.1 Overexertion Risks
Pushing beyond limits can trigger injuries and stress rather than healing.
7.2 Contraindicated Poses
People with high blood pressure should avoid headstands unless supervised.
7.3 Psychological Preparedness
Yoga may bring up repressed emotions; having guidance is important.
8. Extended FAQs
8.1 Can yoga replace therapy?
No, it complements therapy by reducing symptoms and improving coping.
8.2 How long before results show?
Some benefits are immediate, but profound mental changes occur after 6–8 weeks.
8.3 Is yoga safe with medication?
Yes, but consult doctors to avoid conflicts with treatments.
9. YouTube Resource
For guided practice, watch this detailed yoga session for mental health improvement: